What Is Climate Change?Greenhouse effect warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere;Greenhouse effect Planetary warming as a result of the trapping of solar energy beneath atmospheric gases The composition and concentration of the gases in the atmosphere influence the earth's surface temperature because some gases more effectively retain heat than others Fossil fuel combustion, which has increased at a rapid rate since the 1950s, has
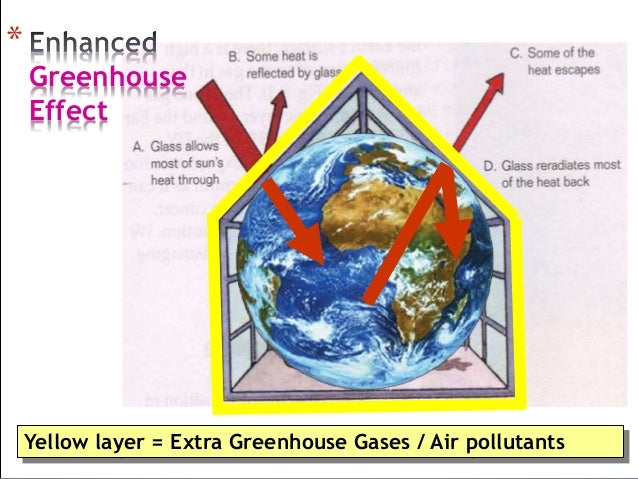
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography
Greenhouse gas definition world geography
Greenhouse gas definition world geography-The greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Geography Standard 8 Understands the characteristics of ecosystems on Earth's surface Standard 14 To begin the class, ask students to think without talking about a definition for the greenhouse effect Give them a minute to formulate their ideas and then have them write down theirThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works
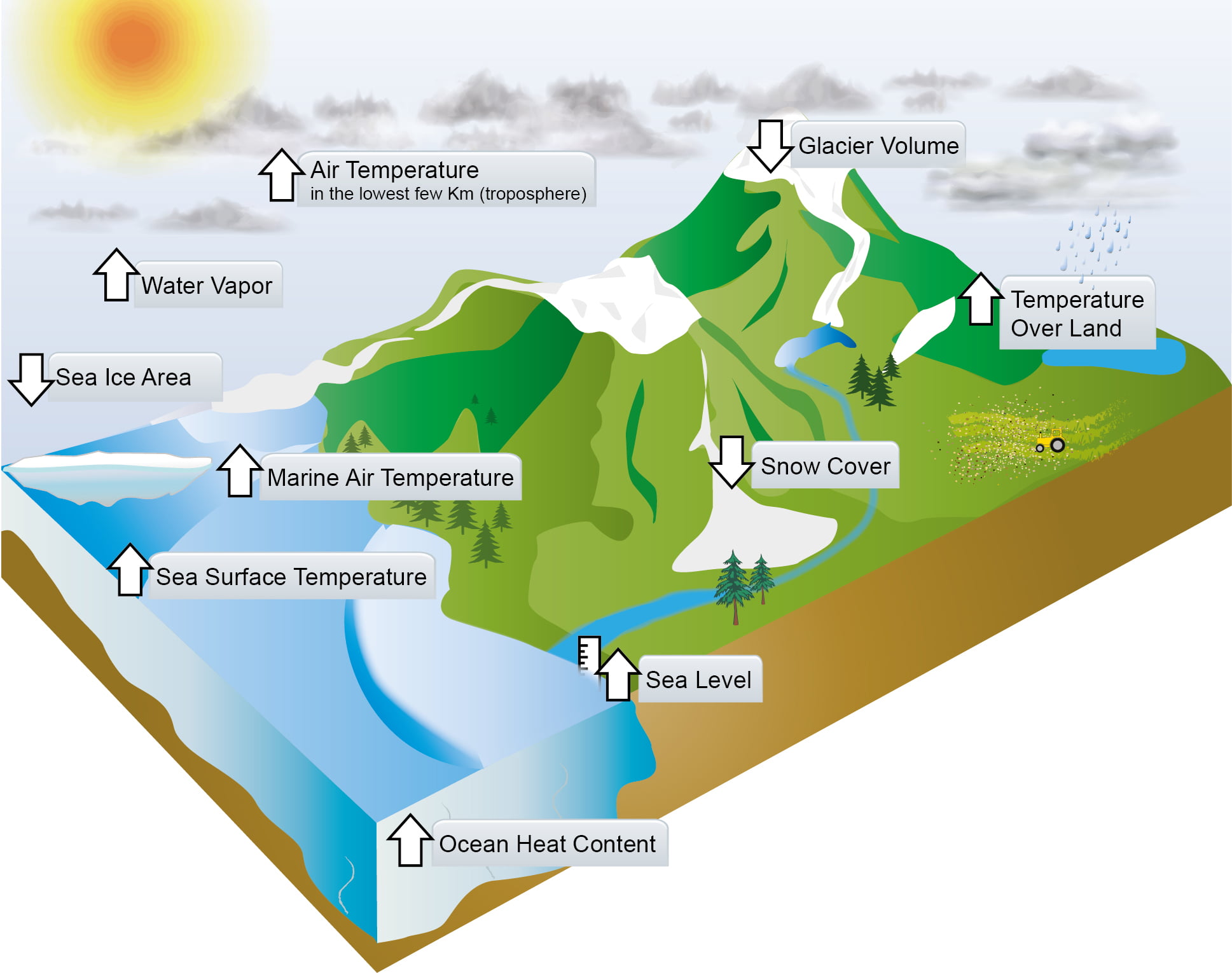



Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Ipcc Updates For Geography Teachers
The greenhouse effect meaning 1 an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere (= mixture of Learn moreThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinated gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphereGreenhouse effect warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere;
Greenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere for long periods, and act as a 'blanket' around the earth absorbing the infrared radiation from the earth and radiating it back to warm the lower atmosphere – the greenhouse effect Without this effect the earth's temperature would be to 30°C colder and less suitable for lifeThe greenhouse effect occurs when certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere (the air around the Earth) trap infrared radiationThis makes the planet become warmer, similar to the way it makes a greenhouse become warmer The greenhouse effect is caused by greenhouse gases;Greenhouse gases absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth's surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives more details
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearThe greenhouse effect is the process in which the emission of infrared radiation by the atmosphere warms a planet's surface The name comes from an analogy with the warming ofGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water




Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
The greenhouse effect is when the Sun's rays penetrate the atmosphere, but when that heat is reflected off the surface cannot escape back into space Gases produced by the burning of fossil fuels prevent the heat from leaving the atmosphere These greenhouse gasses are carbon dioxide, chlorofluorocarbons, water vapor, methane, and nitrous oxideThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gases Greenhouse Earth Overview A "greenhouse Earth" is a period during which no continental glaciers exist anywhere on the planet Additionally, the levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (such as water vapor and methane) are high, and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) range from 28 °C (4 °F) in the tropics to 0 °C (32 °F) in the polar regions




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




2c Carbon Cycle Feedbacks
Caused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface byCaused by atmospheric gases that allow sunshine to pass through but absorb heat that is radiated back from the warmed surface of the earth
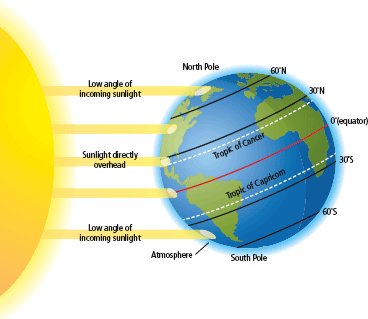



1 Causes Of Global Climate Change The Geographer Online




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
How Do We Measure Sea Level?The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsGlobal warming definition, an increase in the earth's average atmospheric temperature that causes corresponding changes in climate and that may result from the greenhouse effect See more




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



3 1 Factors Affecting Climate Environmental Change Network
GREENHOUSE EFFECT The consequences of the greenhouse effect from desertification to floods #environmental sustainability #nature #climate change Human action is causing an increase in global temperature For that reason, the greenhouse effect, far from being our great ally as was the case in the past, is now a risk to our survivalGreenhouse effect A term used to describe the heating of the atmosphere owing to the presence of carbon dioxide and other gas es Without the presence of these gases, heat from the sun would return to space in the form of infrared radiationHeat emitted from Earth's surface is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere and then reradiated back to the surface Here 100 energy units = 556e24J/year, the total annual solar energy received averages 342 W/m^@ over the




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society



Physical Geography Challenges Of Weather And Climate Revision Cards In Gcse Geography
Earth's vital signs Sea Ice An indicator of changes in the Arctic sea ice minimum over time Arctic sea ice extent both affects and is affected by global climate change Interactive Global Ice Viewer An interactive exploration of how global warming is affecting sea ice, glaciers, and continental ice sheets worldwideGreenhouse Gases and Global Warming Greenhouse gases act as a layering, absorbing IR energy and checking it from dissipating into outer space The effect caused is the slow but steady warming up of Earth's atmosphere and exterior, a process is known as global warming These greenhouse gases include CO2, nitrous oxide (N2O), methane, water A Guide to Climate Change for Kids What's in the Atmosphere?




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Chewvalley Greenhousecms Co Uk Docs Unit 5 Changing Climate Revision Guide Pdf
The most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide(CO 2), and singular noun The greenhouse effect is the problem caused by increased quantities of gases such as carbon dioxide in the air These gases trap the heat from the sun, and cause a gradual rise in the temperature of the Earth's atmosphere COBUILD Advanced English DictionaryThe greenhouse effect from the added water vapor will exacerbate the warming, evaporating more water from the oceans Such amplification of the initial CO2 forcing could conceivably lead to a runaway greenhouse effect where the oceans totally evaporate to the atmosphere and the surface temperature reaches exceedingly high values




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Global Warming
The two large flows on the right represent a kind of energy recycling program that constitutes the greenhouse effect; The natural greenhouse effect The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surfaceThe greenhouse effect of Earth's atmosphere follows some of the same general rules Normally, the atmosphere provides just the right amount of insulation to promote life on the planet The 50 percent of the sun's radiation that reaches the Earth is converted into infrared radiation, or heat Clouds and greenhouse gases — atmospheric com
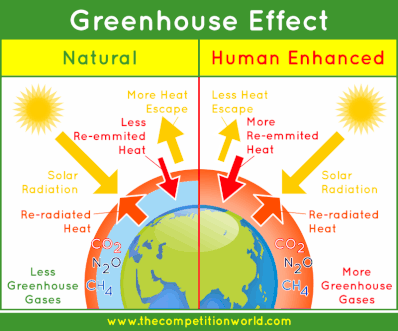



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
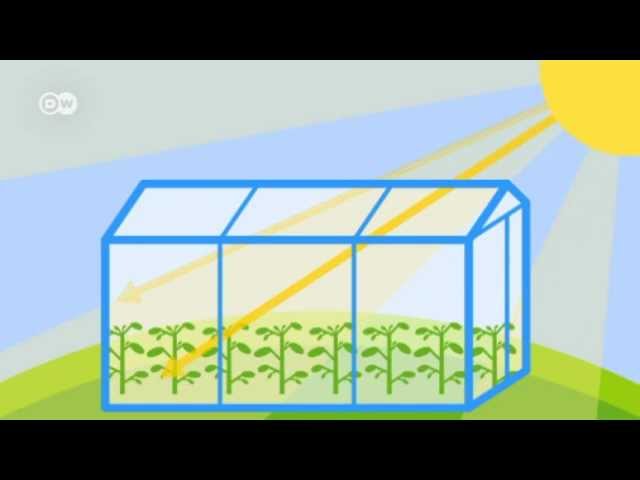



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas Youtube
The greenhouse effect occurs when gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide and CFCs trap heat in the atmosphere by acting as a pane of glass in a car The glass lets the sunlight in to make heat, but when the heat tries to get out the gases absorb the heat Global warming definition is an increase in the earth's atmospheric and oceanic temperatures widely predicted to occur due to an increase in the greenhouse effect resulting especially from pollution How to use global warming in a sentenceAdding more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere enhances the effect, making Earth's surface and lower atmosphere even warmer Image based on a figure from US EPA ( larger version) Greenhouse gases affect Earth's energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth's climate
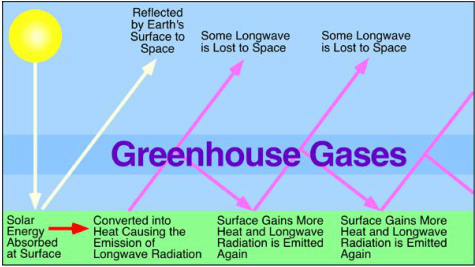



Ess Topic 6 1 Introduction To The Atmosphere Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Gcse Unit 1 Challenges For The Planet Geography Is Easy
Introduction The warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere due to the presence of certain gases in the air is known as the greenhouse effect The gases involved are collectively termed greenhouse gases;How Do Clouds Affect Earth's Climate?Earth's natural greenhouse effect is critical to supporting life Human activities, mainly the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests, have strengthened the greenhouse effect and caused global warming Seasonal and latitudinal dependence of energy balance The Earth's climate is a solar powered system



7 H The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Greenhouse effect, causing global warming The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere, nitrogen (comprising 78% of the dry atmosphere) and oxygen (comprising 21%), exert almost no greenhouse effect Instead, the greenhouse effect comes from molecules that are more complex and much less common Water vapour is the most important greenhouseWhat Is the Greenhouse Effect?See full multimedia package here >> Download highresolution file The basic explanation for why CO2 and other greenhouse gases warm the planet is so simple and has been known science for more than a century Our atmosphere is transparent to




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com
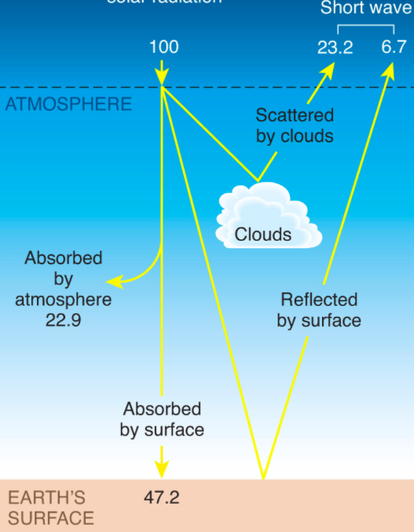



The Energy Balance Geography Myp Gcse Dp
The greenhouse effect is the name given to the natural process that causes the Earth to be warmer than it would be in the absence of an atmosphere Greenhouse gasesFigure 31 The matrix of geographic perspectives Geography's ways of looking at the world—through its focus on place and scale (horizontal axis)—cuts across its three domains of synthesis humansocietal dynamics, environmental dynamics, and environmentalsocietal dynamics (vertical axis)The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist
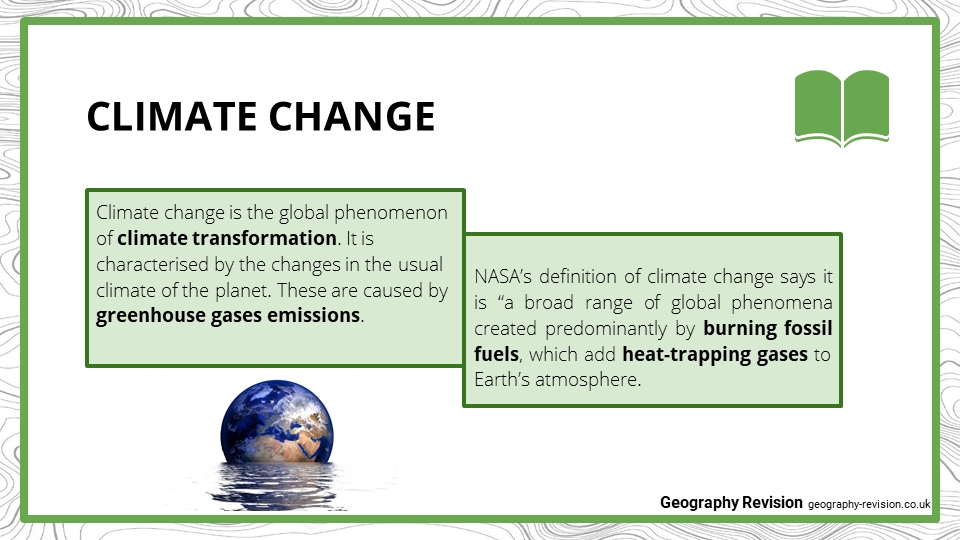



Climate Change Gcse Geography Resources Revision Notes




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society
For every million parts of The Greenhouse Effect climate, climate change, greenhouse effect, greenhouse gases;The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming How the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environment It absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocks It is the raw material for photosynthesis and its carbon is




Heat Transfer In The Atmosphere Physical Geography




The Albedo Effect And The Reflectance Of Solar Heat Geography And You
Greenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many yearsAn atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gasesThe most significant of these are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxideThe greenhouse effect is so named because it resembles the warming of a botanical greenhouse




Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography



The Concept Of Greenhouse Effect Msrblog
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides
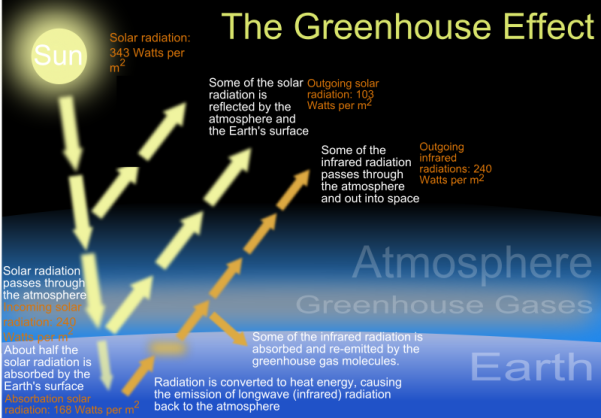



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences
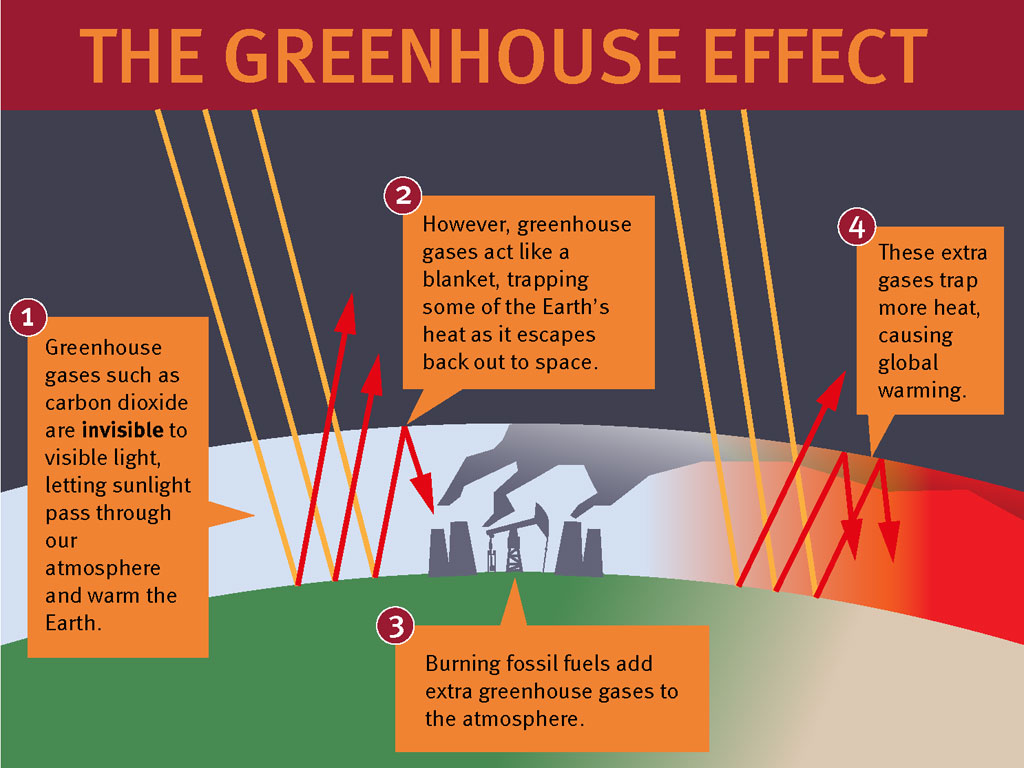



Greenhouse Effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Effects On Envionment Geography For 21 Beyond
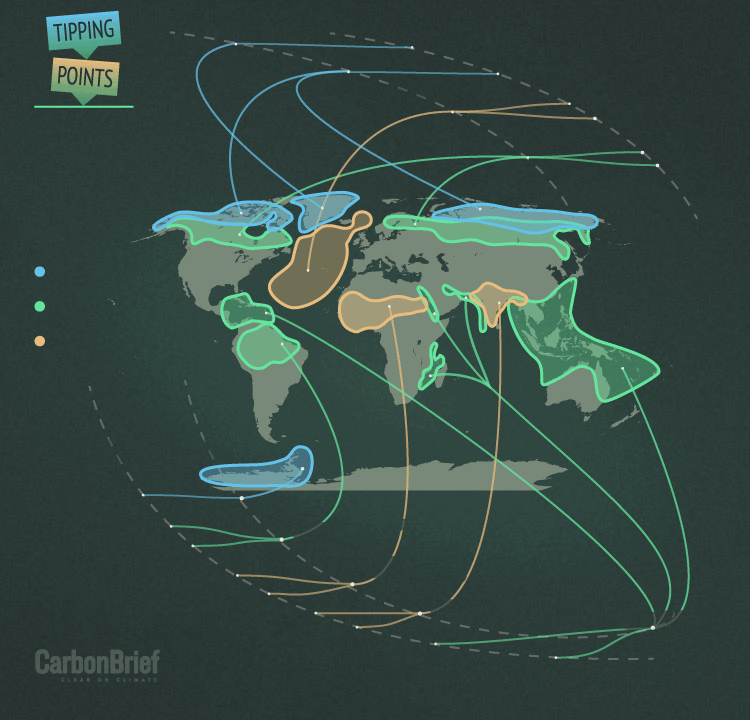



Explainer Nine Tipping Points That Could Be Triggered By Climate Change Carbon Brief
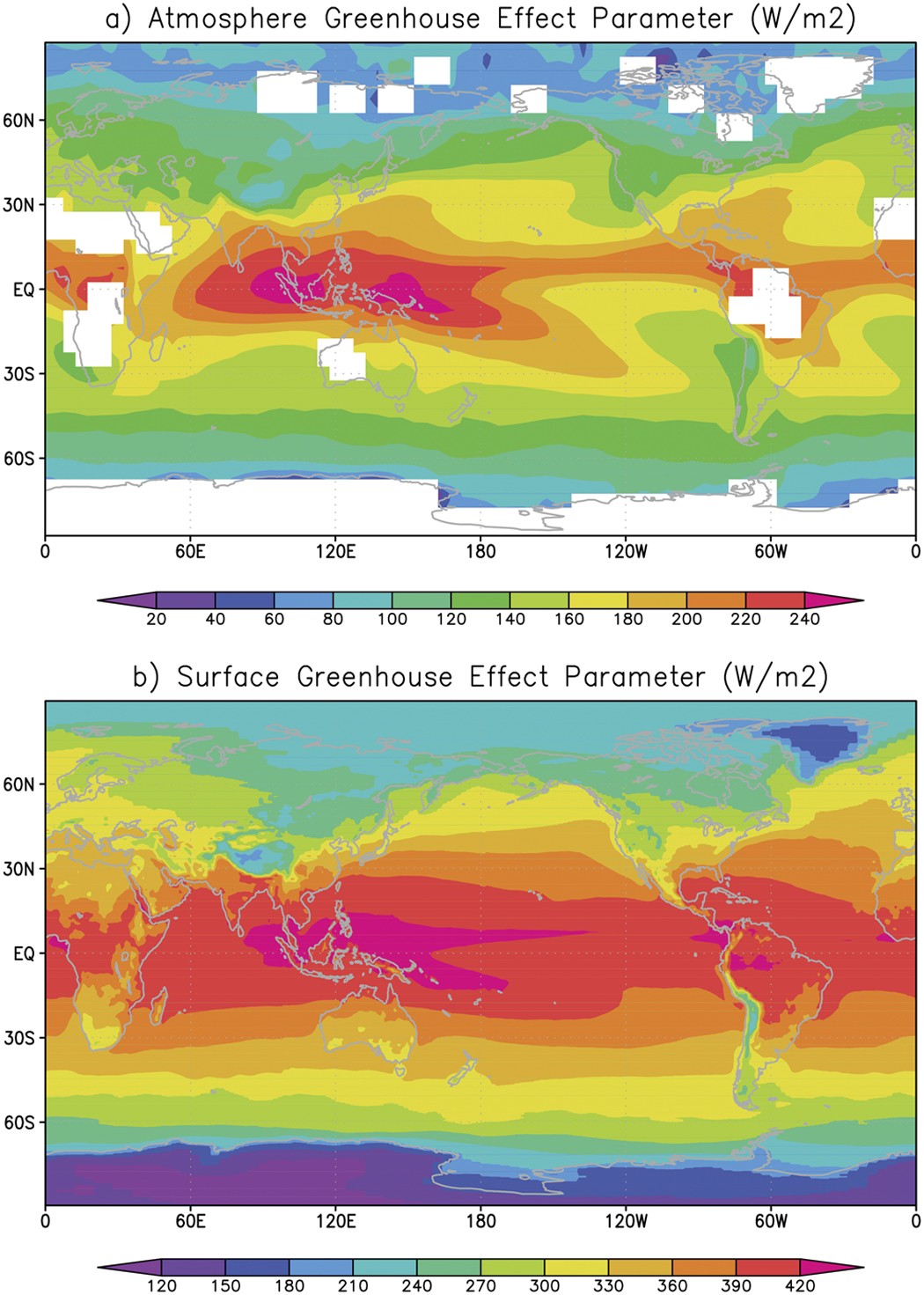



A Hiatus Of The Greenhouse Effect Scientific Reports




Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Ipcc Updates For Geography Teachers
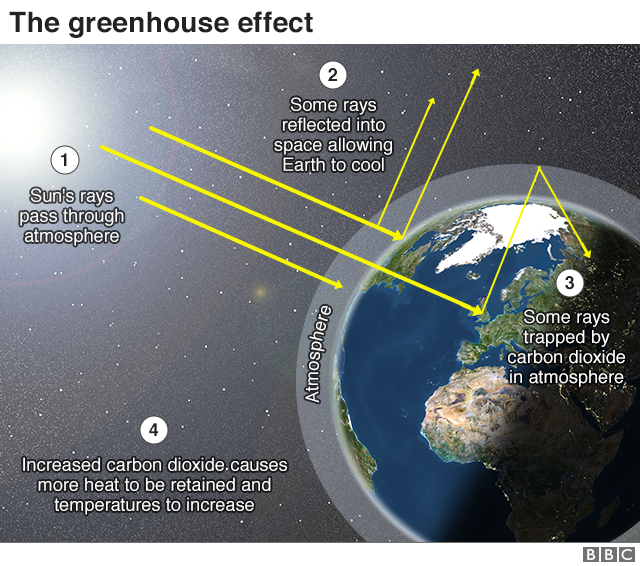



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News



Greenhouse Effect Definition Of Greenhouse Effect By The Free Dictionary



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming
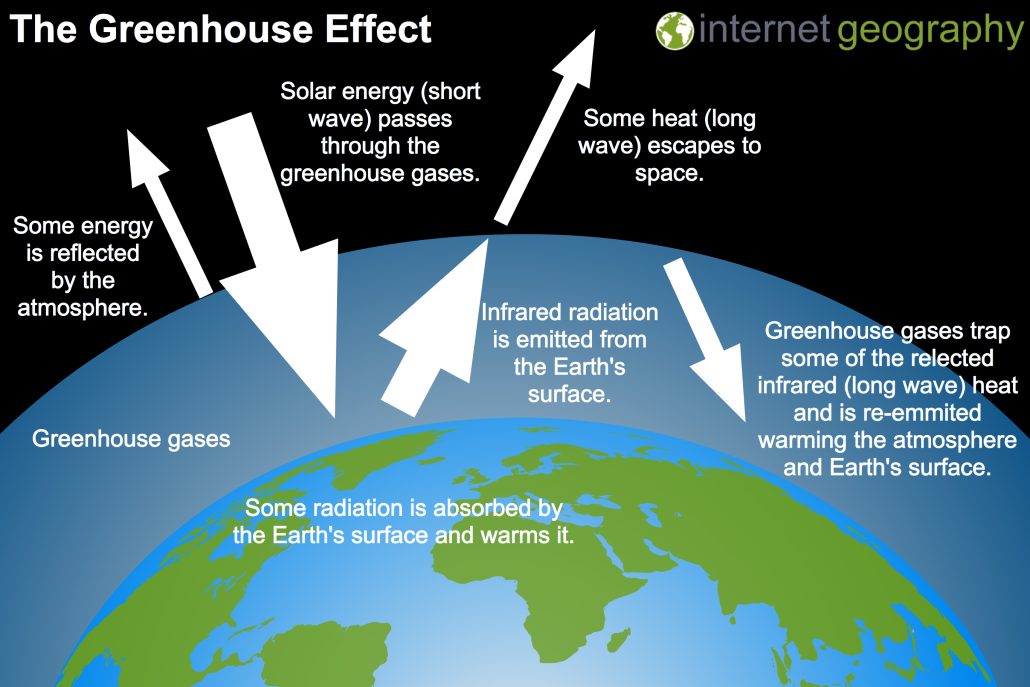



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Edexcel Geography A 9 1 Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
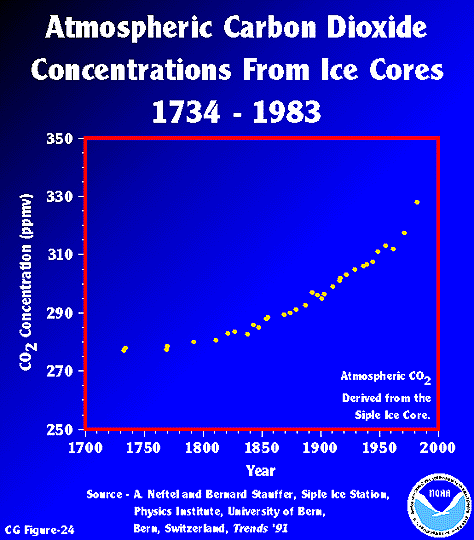



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Youtube
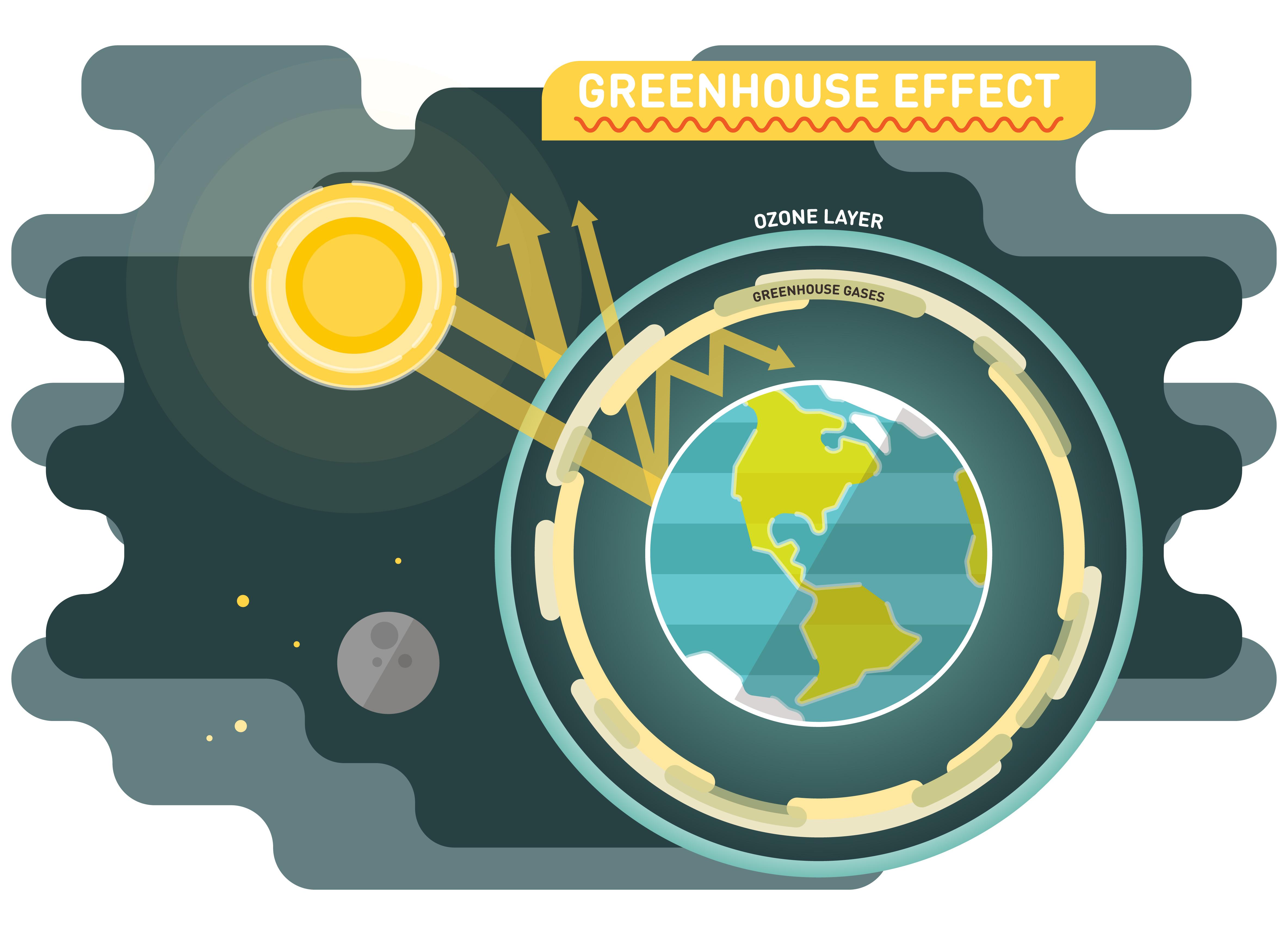



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
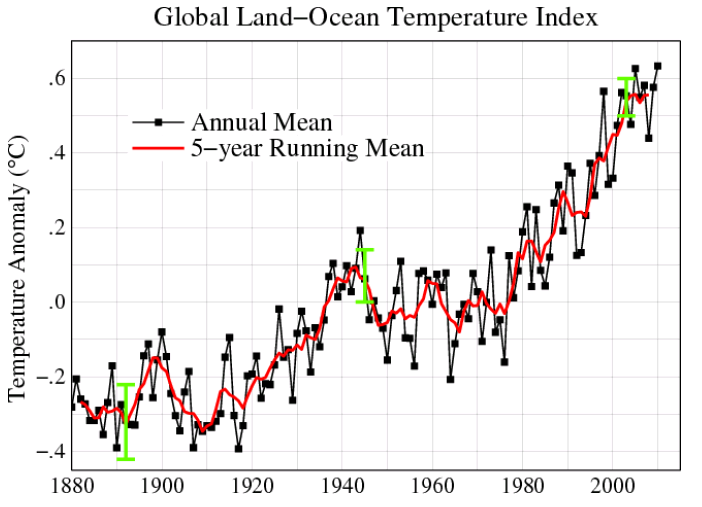



Study Of Impacts Of Global Warming On Climate Change Rise In Sea Level And Disaster Frequency Intechopen




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



Chewvalley Greenhousecms Co Uk Docs Unit 5 Changing Climate Revision Guide Pdf




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Runaway Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Power Point
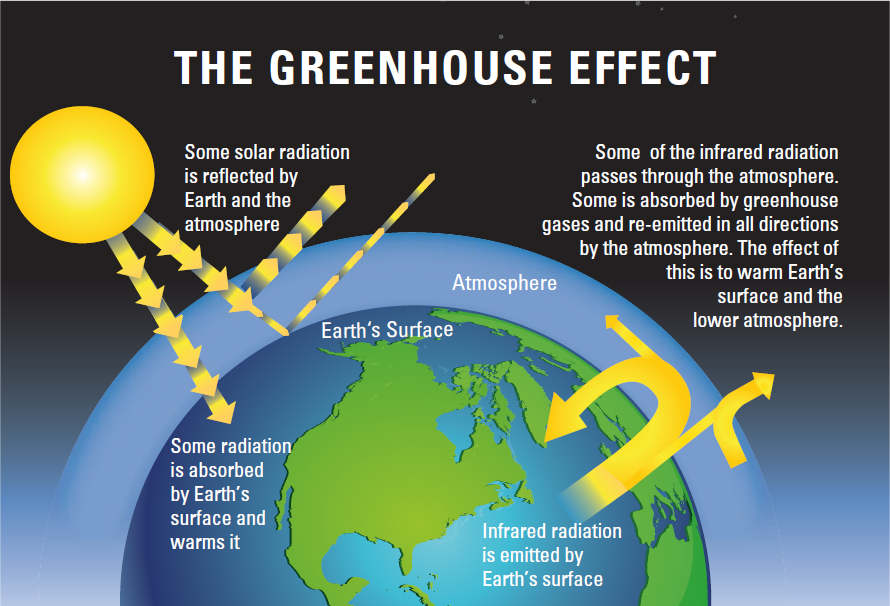



The Basics Of Climate Change Climate Change Evidence And Causes Update The National Academies Press




Global Warming Definition And Meaning Market Business News




How To Stop Global Warming The 8 Best Solutions



1




The Albedo Effect The Influence Of Feedback Mechanisms In Climate Change Youtube
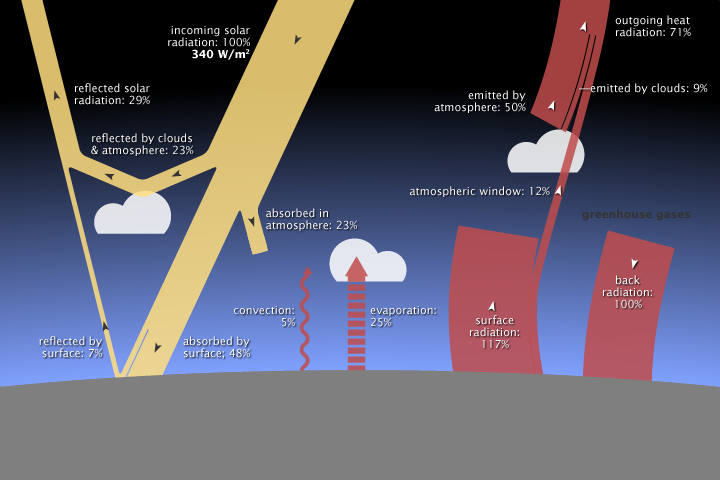



1 Causes Of Global Climate Change The Geographer Online




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



1



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
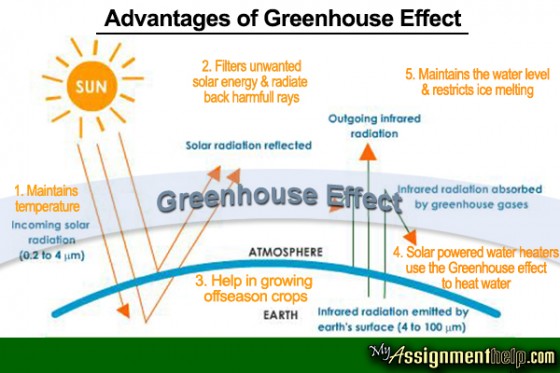



The Greenhouse Effect Know The Advantages And Disadvantages
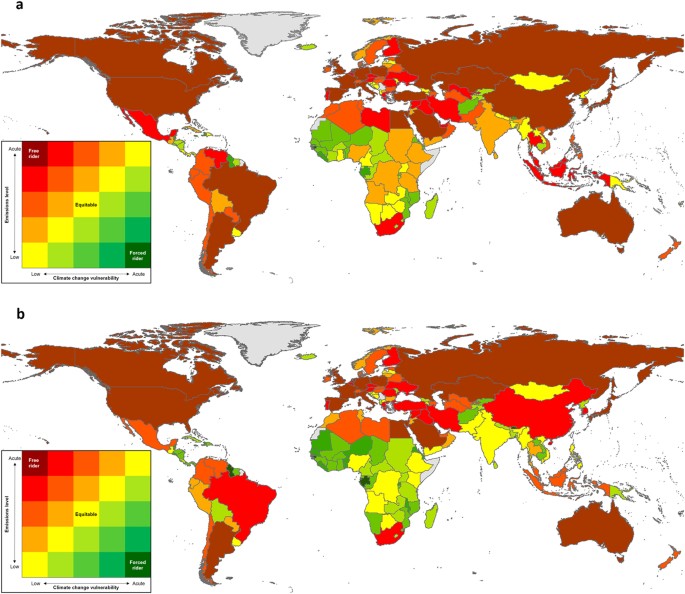



Global Mismatch Between Greenhouse Gas Emissions And The Burden Of Climate Change Scientific Reports
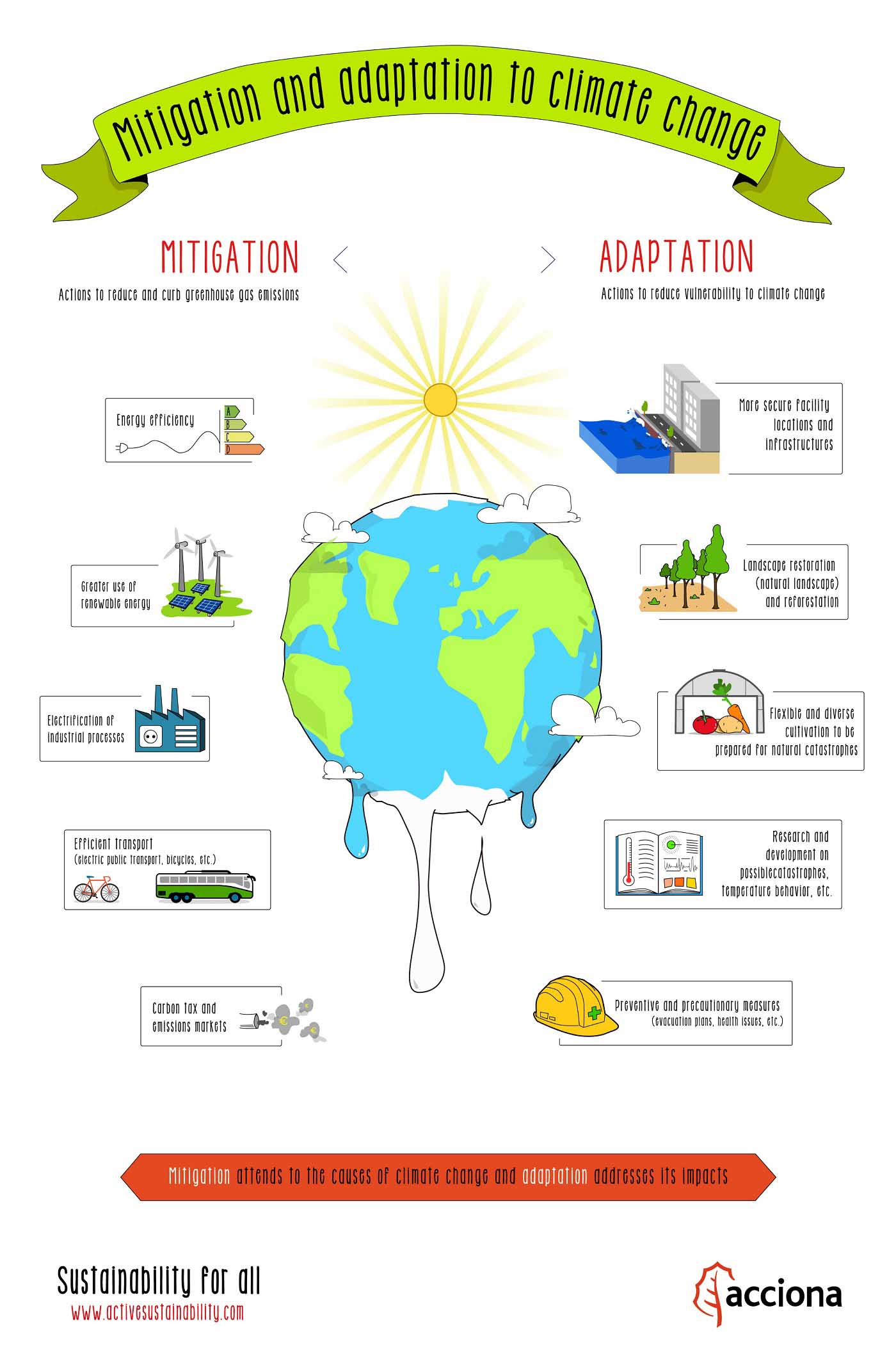



Mitigation And Adaptation To Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
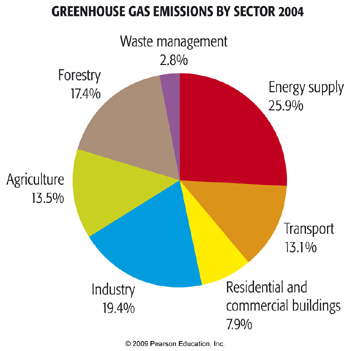



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
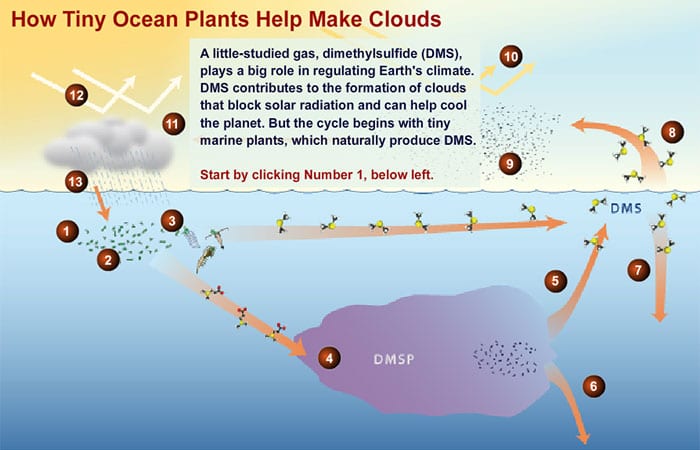



Dms The Climate Gas You Ve Never Heard Of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
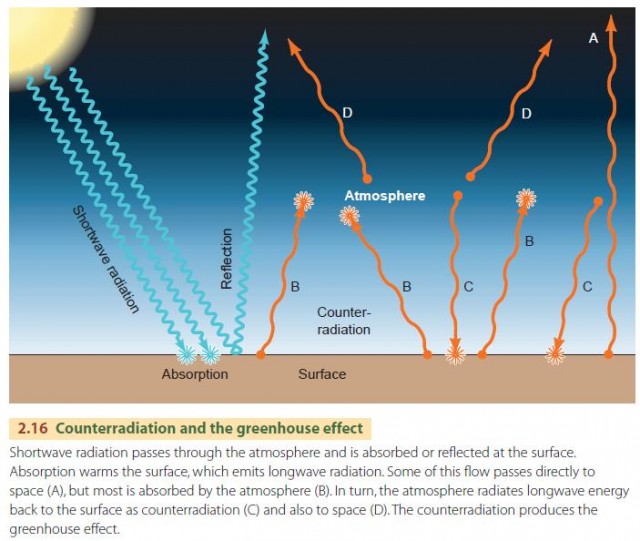



The Global Energy System



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography



1




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences




The Greenhouse Effect Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes




The Greenhouse Effect And Causes Of Climate Change




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Pdf The Greenhouse Effect An Interdisciplinary Perspective
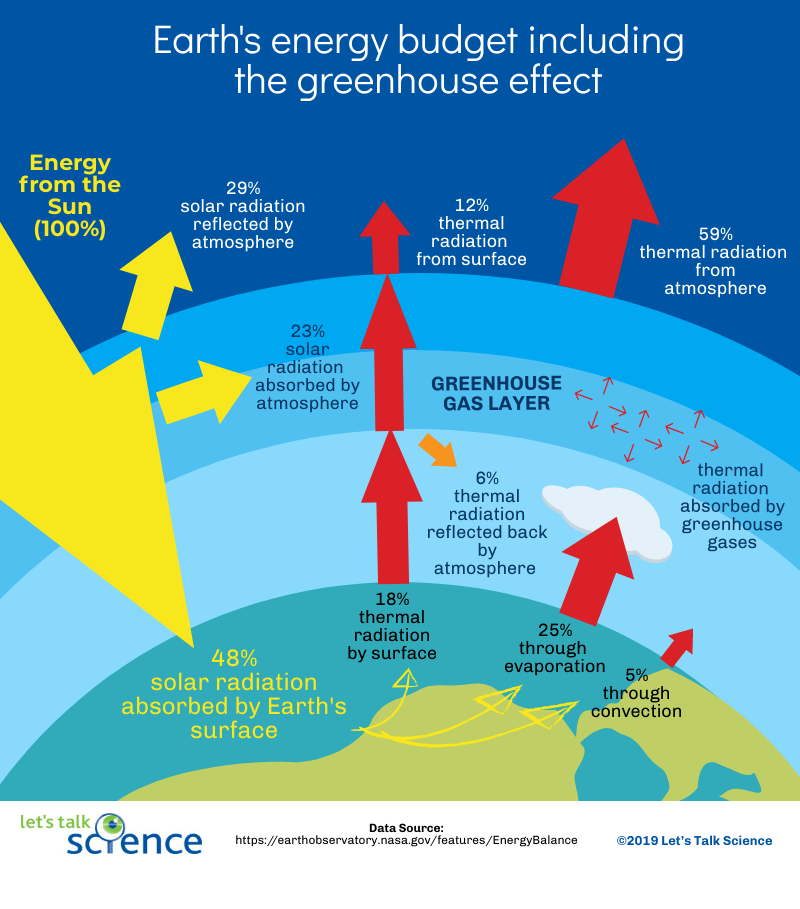



What Is Ocean Warming And Why Does It Matter Let S Talk Science




Global Warming National Geographic Society




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
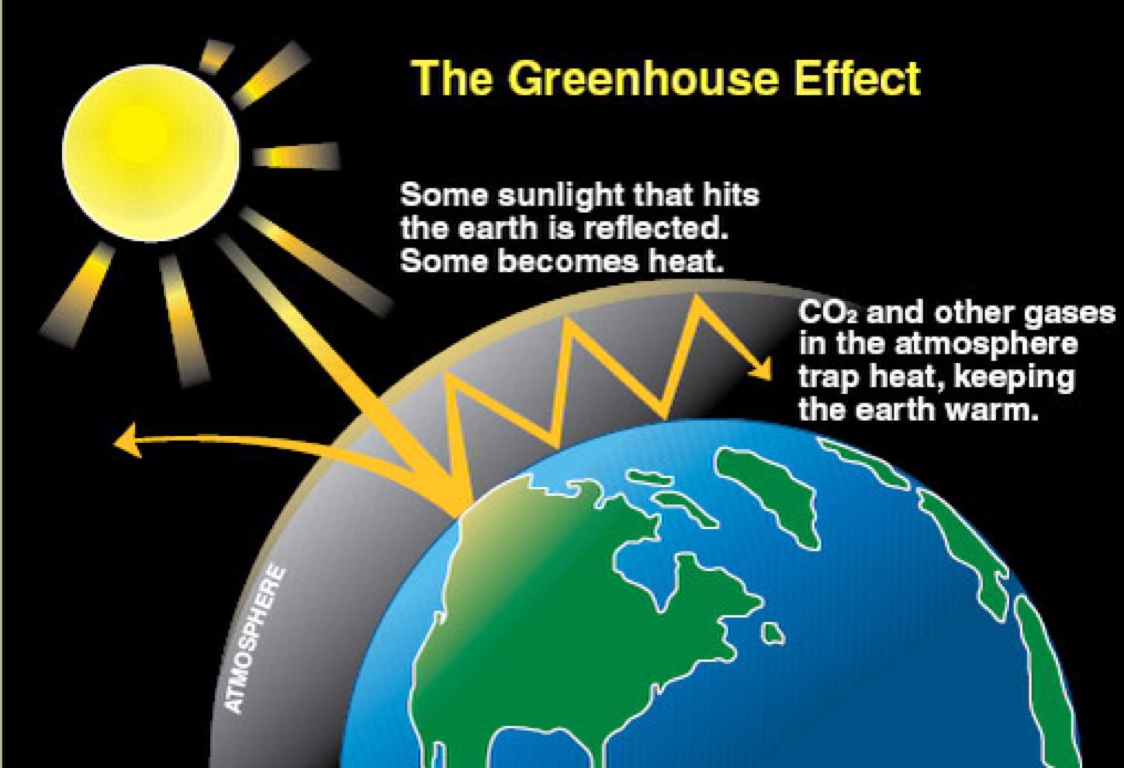



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Geography Finn Valley College




Carbon Emissions The Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Higher Geography Global Warming Ppt Download




Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Gcse Geography Marked By Teachers Com




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
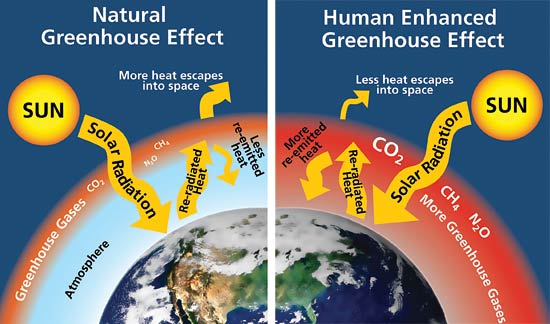



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg



The Causes Of The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And Assessment Of The Difficulties In Reducing Its Impacts International Baccalaureate Geography Marked By Teachers Com



Patterns In Environmental Quality Sustainability Members Area



3



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿